These are the rest of the notes for Posttest 2.
Which battles started the American Revolution? Lexington and Concord
What battle ended the Revolutionary War? Yorktown
Rivers were important to many American Revolution battles.
The Declaration was written because a group of people found they had no choice but to form a new nation.
Who wrote the Declaration of Independence? Thomas Jefferson
The Sons of Liberty were a group of colonists.
Who wrote “Common Sense”? Thomas Paine
Who committed treason? Benedict Arnold
Who was the leader of the Continental Army? George Washington
Who protested the Stamp and Intolerable Acts? Patrick Henry
Who was the second president of the United States? John Adams
Who was the ruler of Great Britain during the American Revolution? King George III
Wednesday, December 7, 2011
Tuesday, December 6, 2011
Posttest 2
**This week's test will be on Friday**
Parents: This week we will take Posttest 2. The entire test will be on the American Revolution. Every student has a study guide to use. This is the first set of notes.
Students: Map Game What we use in class is States 1 Beginner.
Notes for Posttest 2:
When the French and Indian War was over, the Parliament passed laws to tax the colonists because Great Britain needed the colonists to help pay for the war.
What event led to the revolutionary movement in America? The Stamp Act
Why did the Stamp and Tea Acts anger the colonists? The tax money was going to the British government.
The Boston Tea Party occurred because Parliament wanted to give the East India Company a monopoly on tea.
The group formed in the colonies who wanted independence were called the Sons of Liberty.
The colonists had a boycott on British goods. A boycott is a refusal to buy goods.
The colonists refused to pay taxes until they had representation in Parliament. What did the colonists call this? "No taxation without representation"
Since many colonists disagreed about being taxed without having representatives, they refused to buy British goods.
What were the key issues of the American Revolution?
-taxation by the British
-lack of representation
-Intolerable Acts
Parents: This week we will take Posttest 2. The entire test will be on the American Revolution. Every student has a study guide to use. This is the first set of notes.
Students: Map Game What we use in class is States 1 Beginner.
Notes for Posttest 2:
When the French and Indian War was over, the Parliament passed laws to tax the colonists because Great Britain needed the colonists to help pay for the war.
What event led to the revolutionary movement in America? The Stamp Act
Why did the Stamp and Tea Acts anger the colonists? The tax money was going to the British government.
The Boston Tea Party occurred because Parliament wanted to give the East India Company a monopoly on tea.
The group formed in the colonies who wanted independence were called the Sons of Liberty.
The colonists had a boycott on British goods. A boycott is a refusal to buy goods.
The colonists refused to pay taxes until they had representation in Parliament. What did the colonists call this? "No taxation without representation"
Since many colonists disagreed about being taxed without having representatives, they refused to buy British goods.
What were the key issues of the American Revolution?
-taxation by the British
-lack of representation
-Intolerable Acts
Monday, November 28, 2011
American Revolution: Key Figures
Parents: This week's test is on Wednesday. Please review these notes.
Students: Click the name of the person to learn more about them.
George Washington
Benedict Arnold
John Adams
Benjamin Franklin
Liberty Kids site!
Notes for this week's quiz:
King George III:
-King of Great Britain during the American Revolution
-taxed colonists to make money for Great Britain
George Washington
-commander in chief of the Continental Army
-1st President of the United States
Benjamin Franklin
-signed the Declaration of Independence and the Treaty of Paris of 1783
-inventor, scientist, publisher
Patrick Henry
-patriot who protested taxes put on colonists
-famous for saying, "Give me liberty or give me death!"
John Adams
-signed the Declaration of Independence and the Treaty of Paris of 1783
-Vice-President to George Washington, 2nd President of the United States
Benedict Arnold
-Loyalist who was a traitor
-leader in Continental Army and gave secrets to the British
Thomas Jefferson
-wrote the Declaration of Independence
-3rd President of United States
Students: Click the name of the person to learn more about them.
George Washington
Benedict Arnold
John Adams
Benjamin Franklin
Liberty Kids site!
Notes for this week's quiz:
King George III:
-King of Great Britain during the American Revolution
-taxed colonists to make money for Great Britain
George Washington
-commander in chief of the Continental Army
-1st President of the United States
Benjamin Franklin
-signed the Declaration of Independence and the Treaty of Paris of 1783
-inventor, scientist, publisher
Patrick Henry
-patriot who protested taxes put on colonists
-famous for saying, "Give me liberty or give me death!"
John Adams
-signed the Declaration of Independence and the Treaty of Paris of 1783
-Vice-President to George Washington, 2nd President of the United States
Benedict Arnold
-Loyalist who was a traitor
-leader in Continental Army and gave secrets to the British
Thomas Jefferson
-wrote the Declaration of Independence
-3rd President of United States
Monday, November 14, 2011
American Revolution: Yorktown
Parents: This week we are back to our normal routine of testing on Wednesdays. This week's quiz will be a review of everything learned on the American Revolution thus far. Please refer to all previous post,as well as the new notes for this week.
Notes for this week's quiz:
What is a traitor? someone who goes against their government
What was the last battle of the Revolutionary War? Yorktown
Who won the Revolutionary War? Americans
What actually ended the American Revolution? the signing of the Treaty of Paris
Notes for this week's quiz:
What is a traitor? someone who goes against their government
What was the last battle of the Revolutionary War? Yorktown
Who won the Revolutionary War? Americans
What actually ended the American Revolution? the signing of the Treaty of Paris
Monday, November 7, 2011
The Declaration of Independence
**This week's test will be on Thursday.**
Parents: This week's test will be over the Declaration of Independence. The students have a graphic organizer and handouts to study from.
Students: Here are some links to learn more about the Declaration.
A lot of information!
Congress for Kids
Games and Information
Notes for this week's test:
Who wrote the Declaration of Independence? Thomas Jefferson
Why did the Declaration need to be written? the colonists needed to declare independence from Great Britain
What 3 things does the Declaration give to all Americans? life, liberty, and the pursuit of happiness
Who signed the Declaration? all members of the Second Continental Congress
What kind of material was the declaration written on? parchment
Who signed their name the largest on the Declaration? John Hancock
What did the signing of the Declaration mean for the colonists? they had the right to be free from the king and start a new nation
When was the Declaration signed? July 4, 1776
How many colonies wanted to be independent from Great Britan? 13
Who was on the writing committee of the Declaration with Thomas Jefferson? John Adams, Benjamin Franklin, Robert Livingston, and Roger Sherman
Parents: This week's test will be over the Declaration of Independence. The students have a graphic organizer and handouts to study from.
Students: Here are some links to learn more about the Declaration.
A lot of information!
Congress for Kids
Games and Information
Notes for this week's test:
Who wrote the Declaration of Independence? Thomas Jefferson
Why did the Declaration need to be written? the colonists needed to declare independence from Great Britain
What 3 things does the Declaration give to all Americans? life, liberty, and the pursuit of happiness
Who signed the Declaration? all members of the Second Continental Congress
What kind of material was the declaration written on? parchment
Who signed their name the largest on the Declaration? John Hancock
What did the signing of the Declaration mean for the colonists? they had the right to be free from the king and start a new nation
When was the Declaration signed? July 4, 1776
How many colonies wanted to be independent from Great Britan? 13
Who was on the writing committee of the Declaration with Thomas Jefferson? John Adams, Benjamin Franklin, Robert Livingston, and Roger Sherman
Tuesday, November 1, 2011
American Revolution: The Battles of Lexington and Concord & Bunker Hill
**This week we will be testing on Thursday.**
Parents: This week's quiz will be a review over everything we have covered thus far on the American Revolution. Please review all previous post! The information continues to become more difficult and needs to be reviewed.
Notes for this week's quiz: *Please see all post on American Revolution*
Who rode ahead of the British to warn the Minutemen that the British were coming? Paul Revere
The battle of Lexington and Concord was the __________ battle of the American Revolution. first
The battle of Lexington and Concord was known as ______________. "the shot heard round the world"
Who were Minutemen? colonists who were ready to fight in a minute
Who fought in The Battle of Bunker Hill? colonists and the British
Who won The Battle of Bunker Hill? the British
Parents: This week's quiz will be a review over everything we have covered thus far on the American Revolution. Please review all previous post! The information continues to become more difficult and needs to be reviewed.
Notes for this week's quiz: *Please see all post on American Revolution*
Who rode ahead of the British to warn the Minutemen that the British were coming? Paul Revere
The battle of Lexington and Concord was the __________ battle of the American Revolution. first
The battle of Lexington and Concord was known as ______________. "the shot heard round the world"
Who were Minutemen? colonists who were ready to fight in a minute
Who fought in The Battle of Bunker Hill? colonists and the British
Who won The Battle of Bunker Hill? the British
American Revolution: First and Second Continental Congress
Notes for this week's quiz:
What were the First the Second Continental Congress? a group of representatives from the 13 colonies
The members of Congress were _____________. colonists
The Second Continental Congress suggested that___________________ should be the commander in chief of all military forces in the colonies. George Washington
What is a commander in chief? leader of all military services
If someone extends an 'olive branch,' what are they asking for? peace
What were the First the Second Continental Congress? a group of representatives from the 13 colonies
The members of Congress were _____________. colonists
The Second Continental Congress suggested that___________________ should be the commander in chief of all military forces in the colonies. George Washington
What is a commander in chief? leader of all military services
If someone extends an 'olive branch,' what are they asking for? peace
Tuesday, October 25, 2011
American Revolution: Boston Tea Party & Intolerable Acts
Parents: This week's quiz will be over the Boston Tea Party and the Intolerable Acts.
Notes for this week's quiz:
What date did the Boston Tea Party take place? December 16, 1773
Who was responsible for the Boston Tea Party? Sons of Liberty
What were the men disguised as that dumped the tea overboard? Indians
Why did the Boston Tea Party happen? the colonists had a protest on tea
What was a result of the Boston Tea Party? Parliament created the Intolerable Acts
What was the purpose of the Intolerable Acts? to punish the colonists
What did the Intolerable Acts include? blockading and quartering
What was the result of the Intolerable Acts? the First Continental Congress was formed
Who were the Sons of Liberty? group of ordinary colonists who protested taxes
Who is the Parliament? British Congress
What does intolerable mean? unacceptable
What is a blockade? when ships block other ships from entering or leaving a harbor
Notes for this week's quiz:
What date did the Boston Tea Party take place? December 16, 1773
Who was responsible for the Boston Tea Party? Sons of Liberty
What were the men disguised as that dumped the tea overboard? Indians
Why did the Boston Tea Party happen? the colonists had a protest on tea
What was a result of the Boston Tea Party? Parliament created the Intolerable Acts
What was the purpose of the Intolerable Acts? to punish the colonists
What did the Intolerable Acts include? blockading and quartering
What was the result of the Intolerable Acts? the First Continental Congress was formed
Who were the Sons of Liberty? group of ordinary colonists who protested taxes
Who is the Parliament? British Congress
What does intolerable mean? unacceptable
What is a blockade? when ships block other ships from entering or leaving a harbor
Friday, October 21, 2011
BIG Thank You
Parents: For the past three weeks, the students have been writing letters to soldiers over seas. These letters are meant to be a thank you to the soldiers for their service.
We are working with a radio station who is trying to get 400,000 letters by next week. This project is called 'The Big Thank You.' Their goal is to have a letter sent to every soldier who is serving overseas.
The students have written 374 letters total!!!! I am so proud of their effort and willingness to do this! Give your child a pat on the back!
We are working with a radio station who is trying to get 400,000 letters by next week. This project is called 'The Big Thank You.' Their goal is to have a letter sent to every soldier who is serving overseas.
The students have written 374 letters total!!!! I am so proud of their effort and willingness to do this! Give your child a pat on the back!
Monday, October 17, 2011
American Revolution: French and Indian War
Parents: This week's quiz will cover the French and Indian War, Sugar Act, Stamp Act, and The Boston Massacre. Every student has a graphic organizer with this information. Next week's quiz will repeat this information, as well as new information covered.
**Make sure your children are reviewing whatever notes they have every night. This information will continue to get more difficult!
Notes for this week's quiz:
Who fought in the French and Indian War? French and British
Who won the French and Indian War? British
What was the purpose of the French and Indian War? The French and the British both wanted land west of the Appalachian Mountains.
What did the king do after the British won the war? issued a proclamation telling colonists they could not move to the new territory
Why was the Sugar Act put in place? England needed a way to pay the debt from the war.
What did the Sugar Act tax? sugar
What did the Stamp Act tax? newspapers & legal documents
The Stamp Act Congress was formed to get rid of the Stamp Act. They wrote a declaration to the King George to get the Stamp Act repealed. What does repealed mean?
canceled; done away with
Who was shot in The Boston Massacre? colonists
What is the correct sequence of events? French and Indian War, Sugar Act, Stamp Act, The Boston Massacre
**Make sure your children are reviewing whatever notes they have every night. This information will continue to get more difficult!
Notes for this week's quiz:
Who fought in the French and Indian War? French and British
Who won the French and Indian War? British
What was the purpose of the French and Indian War? The French and the British both wanted land west of the Appalachian Mountains.
What did the king do after the British won the war? issued a proclamation telling colonists they could not move to the new territory
Why was the Sugar Act put in place? England needed a way to pay the debt from the war.
What did the Sugar Act tax? sugar
What did the Stamp Act tax? newspapers & legal documents
The Stamp Act Congress was formed to get rid of the Stamp Act. They wrote a declaration to the King George to get the Stamp Act repealed. What does repealed mean?
canceled; done away with
Who was shot in The Boston Massacre? colonists
What is the correct sequence of events? French and Indian War, Sugar Act, Stamp Act, The Boston Massacre
Wednesday, October 12, 2011
American Revolution
*Vocabulary Quiz on Friday*
Parents: We have ended our first nine week period and are now beginning a new unit. We will cover all of the American Revolution. This information is going to be very hard for the students to learn and remember. They should be reviewing all the notes they have every night.
This week's test will be over vocabulary we have been discussing this week. Each student should have their words written down to study.
Next week we will move back to our regular schedule of test on Wednesdays.
Notes for this week's test:
Fort: a structure built for protection in battle
People in a battle will build ____________ for protection.
Fork: when two rivers come together to make a third
The French built a fort at the ____________ of the Ohio River.
Revolution: sudden change(changing the government)
The colonists wanted to start a ______________ because they wanted to start their own government.
Parliament: lawmaking body of British government (like our Congress)
The colonists wanted to have representatives in the British ________________.
Allies: friends in war
Many French and Native Americans were ____________ in the French and Indian War.
Alliance: formal agreement between groups, nations, individuals, etc...
The French and Native Americans formed an _______________ during the French and Indian War.
Repeal: cancel
The Stamp Act was ________________ in 1766 after The Stamp Act Congress wrote a declaration to the king.
Boycott: refuse to buy
The colonists had a ______________on British goods because they did not want to pay the taxes on those goods.
Declaration: formal statement
The Stamp Act Congress wrote a _______________ to the king of Britain to repeal the Stamp Act.
Liberty: freedom to chose your own government
The colonists were fighting for ______________. They wanted freedom from Britain's rule.
Parents: We have ended our first nine week period and are now beginning a new unit. We will cover all of the American Revolution. This information is going to be very hard for the students to learn and remember. They should be reviewing all the notes they have every night.
This week's test will be over vocabulary we have been discussing this week. Each student should have their words written down to study.
Next week we will move back to our regular schedule of test on Wednesdays.
Notes for this week's test:
Fort: a structure built for protection in battle
People in a battle will build ____________ for protection.
Fork: when two rivers come together to make a third
The French built a fort at the ____________ of the Ohio River.
Revolution: sudden change(changing the government)
The colonists wanted to start a ______________ because they wanted to start their own government.
Parliament: lawmaking body of British government (like our Congress)
The colonists wanted to have representatives in the British ________________.
Allies: friends in war
Many French and Native Americans were ____________ in the French and Indian War.
Alliance: formal agreement between groups, nations, individuals, etc...
The French and Native Americans formed an _______________ during the French and Indian War.
Repeal: cancel
The Stamp Act was ________________ in 1766 after The Stamp Act Congress wrote a declaration to the king.
Boycott: refuse to buy
The colonists had a ______________on British goods because they did not want to pay the taxes on those goods.
Declaration: formal statement
The Stamp Act Congress wrote a _______________ to the king of Britain to repeal the Stamp Act.
Liberty: freedom to chose your own government
The colonists were fighting for ______________. They wanted freedom from Britain's rule.
Monday, October 3, 2011
Posttest 1
**Posttest 1 Thursday**
Parents: We will take Posttest 1 on Thursday. I have made study guides for every student that have all the information they need.
Students: Here is the website we used in class about Colonial America.
Notes for Posttest 1:
Native Americans
When the _________ died, it led to the permanent elimination of some villages of Native American tribes. buffalo
Which Native American tribe went whale hunting? Inuit
The Pawnee lived in dome shaped houses because ______________. it kept them cool in summer and warm in winter
Why didn’t Europeans and Native Americans get along? they competed for land
How did the Native Americans NOT help Explorers? they competed for land
Explorers
What were all European explorers in search of? a short trade route to Asia
Who sailed with Columbus and founded Florida? Juan Ponce de Leon
Who discovered the Americas? Christopher Columbus
What explorer traded with Native Americans? John Cabot
What continent were all Europeans in search of and eager to trade with? Asia
Colonial Life
If you lived on a plantation and owned slaves, you would be in a __________ colony. Southern
Why were the middle colonies nicknamed the ‘breadbasket colonies’? it had good soil and a good climate to grow crops
What colonies had poor farming because they had thin, rocky soil? New England
What shows how specialization improved the standards of living in the New England colonies? (How did they make money?)shipbuilding
________were not taken against their will and were given freedom after a certain length of time. Indentured servants
Voluntary exchange = bartering
trade off = voluntary exchange
Parents: We will take Posttest 1 on Thursday. I have made study guides for every student that have all the information they need.
Students: Here is the website we used in class about Colonial America.
Notes for Posttest 1:
Native Americans
When the _________ died, it led to the permanent elimination of some villages of Native American tribes. buffalo
Which Native American tribe went whale hunting? Inuit
The Pawnee lived in dome shaped houses because ______________. it kept them cool in summer and warm in winter
Why didn’t Europeans and Native Americans get along? they competed for land
How did the Native Americans NOT help Explorers? they competed for land
Explorers
What were all European explorers in search of? a short trade route to Asia
Who sailed with Columbus and founded Florida? Juan Ponce de Leon
Who discovered the Americas? Christopher Columbus
What explorer traded with Native Americans? John Cabot
What continent were all Europeans in search of and eager to trade with? Asia
Colonial Life
If you lived on a plantation and owned slaves, you would be in a __________ colony. Southern
Why were the middle colonies nicknamed the ‘breadbasket colonies’? it had good soil and a good climate to grow crops
What colonies had poor farming because they had thin, rocky soil? New England
What shows how specialization improved the standards of living in the New England colonies? (How did they make money?)shipbuilding
________were not taken against their will and were given freedom after a certain length of time. Indentured servants
Voluntary exchange = bartering
trade off = voluntary exchange
Sunday, September 25, 2011
Colonial Life
**Test on Tuesday and Thursday this week**
Parents: This week's test will be over life in Colonial America. The students have a few different graphic organizers that they can use to study. The students will be tested on Tuesday and Thursday of this week. Tuesday's test will be over labeling the original 13 Colonies and telling me which colonies make up each region. Every student has a map that we made in class to use to study. Thursday's test will be the weekly test.
Students: Use this link to review your colonies. Click on each colony to see it's facts.
You can do activities and play games with the 13 colonies here.
Use this link to find out what life was like for children and for different workers in Colonial America.
*Next week we will begin reviewing for Posttest 1. It will be given the following week.
Notes for this week's quiz:
Why did settlers want to come to America? economic opportunity and religions freedom
What does religious freedom mean? the freedom to practice whatever religion you want
What is a self-sustaining farmer? a farmer who grows crops for himself
What is a cash crop? crops grown to make money
What is an indentured servant? a person who would work in exchange for a trip to the New World (usually working for 7 years)
What is a navigable river? a river that is deep & wide enough for a ship to get down
What is a plantation? a large piece of land that would include a farm, master's house, and slaves houses
New England Colonies: Massachusetts, New Hampshire, Connecticut, & Rhode Island
-thin, rocky soil that was not good for growing crops
-shipbuilding made the people of New England successful
-not navigable rivers
-self-sustaining farmers
-community minded (they took care of each other; distrusted outsiders)
-against slavery
Middle (Mid-Atlantic) Colonies: New York, Pennsylvania, New Jersey, & Delaware
-flat land that was great for farming; especially grains and wheat
-nicknamed "the bread basket colonies"
-navigable river that allowed them to trade with other regions
-people were open-minded
-people had religious and economic freedom
-against slavery and helped slaves escape the South
Southern Colonies: Virginia, Maryland, North Carolina, South Carolina, & Georgia
-flat land that was great for farming
-cash crops made the southern colonies successful: tobacco, indigo, & sugar
-navigable rivers
-people were close-minded and not willing to change
-people lived on plantations
-settlers imported slaves to work on the plantations
Parents: This week's test will be over life in Colonial America. The students have a few different graphic organizers that they can use to study. The students will be tested on Tuesday and Thursday of this week. Tuesday's test will be over labeling the original 13 Colonies and telling me which colonies make up each region. Every student has a map that we made in class to use to study. Thursday's test will be the weekly test.
Students: Use this link to review your colonies. Click on each colony to see it's facts.
You can do activities and play games with the 13 colonies here.
Use this link to find out what life was like for children and for different workers in Colonial America.
*Next week we will begin reviewing for Posttest 1. It will be given the following week.
Notes for this week's quiz:
Why did settlers want to come to America? economic opportunity and religions freedom
What does religious freedom mean? the freedom to practice whatever religion you want
What is a self-sustaining farmer? a farmer who grows crops for himself
What is a cash crop? crops grown to make money
What is an indentured servant? a person who would work in exchange for a trip to the New World (usually working for 7 years)
What is a navigable river? a river that is deep & wide enough for a ship to get down
What is a plantation? a large piece of land that would include a farm, master's house, and slaves houses
New England Colonies: Massachusetts, New Hampshire, Connecticut, & Rhode Island
-thin, rocky soil that was not good for growing crops
-shipbuilding made the people of New England successful
-not navigable rivers
-self-sustaining farmers
-community minded (they took care of each other; distrusted outsiders)
-against slavery
Middle (Mid-Atlantic) Colonies: New York, Pennsylvania, New Jersey, & Delaware
-flat land that was great for farming; especially grains and wheat
-nicknamed "the bread basket colonies"
-navigable river that allowed them to trade with other regions
-people were open-minded
-people had religious and economic freedom
-against slavery and helped slaves escape the South
Southern Colonies: Virginia, Maryland, North Carolina, South Carolina, & Georgia
-flat land that was great for farming
-cash crops made the southern colonies successful: tobacco, indigo, & sugar
-navigable rivers
-people were close-minded and not willing to change
-people lived on plantations
-settlers imported slaves to work on the plantations
Sunday, September 18, 2011
European and Native American Conflict
Parents: This week's quiz will be over all of the explorers we learned and a few questions about European and Native American conflict. We will be beginning to learn about the formation of the 13 Colonies this week.
Notes for this week's quiz:
(Use explorer notes posted last week)
How did Pocahontas help the colonists and Native Americans communicate? she translated for them
What did Europeans think they could find in the Americas? gold
What did the Europeans and Native Americans compete for? land
Native Americans had to teach the settlers how to _____________. grow crops
Notes for this week's quiz:
(Use explorer notes posted last week)
How did Pocahontas help the colonists and Native Americans communicate? she translated for them
What did Europeans think they could find in the Americas? gold
What did the Europeans and Native Americans compete for? land
Native Americans had to teach the settlers how to _____________. grow crops
Thursday, September 8, 2011
European Explorers
Parents: We have finished Native Americans and are now moving on to European Explorers. We will cover six different explorers over the next two weeks. Next week the students will be tested on basic information about each explorer.
*Every student has a graphic organizer with this information on it.
To learn more about each explorer click on their names.
Christopher Columbus , John Cabot, Juan Ponce de Leon, Vasco Nunez de Balboa, Jacques Cartier, Henry Hudson
Notes for this week's quiz:
Christopher Columbus:
-1492
-sponsor was Spain
-His purpose was to sail west to reach Asia.
John Cabot:
-1497
-sponsor was England
-He reached the eastern coast of Canada where fish were plentiful.
Juan Ponce de Leon:
-1513
-sponsor was Spain
-He wanted to find gold and the 'fountain of youth.'
-He ended up in Florida where the Native Americans were.
Vasco Nunez de Balboa:
-1531
-sponsor was Spain
-He was the first to cross Panama to reach the Pacific Ocean.
Jacques Cartier:
-1531
-sponsor was France
-He sailed over 1,000 miles down the St. Lawrence River in Canada.
Henry Hudson:
-1607
-sponsor was England
-He sailed up the Hudson River in New York, but his crew turned against him.
What did a sponsor do for the explorers? paid for their trips
*Every student has a graphic organizer with this information on it.
To learn more about each explorer click on their names.
Christopher Columbus , John Cabot, Juan Ponce de Leon, Vasco Nunez de Balboa, Jacques Cartier, Henry Hudson
Notes for this week's quiz:
Christopher Columbus:
-1492
-sponsor was Spain
-His purpose was to sail west to reach Asia.
John Cabot:
-1497
-sponsor was England
-He reached the eastern coast of Canada where fish were plentiful.
Juan Ponce de Leon:
-1513
-sponsor was Spain
-He wanted to find gold and the 'fountain of youth.'
-He ended up in Florida where the Native Americans were.
Vasco Nunez de Balboa:
-1531
-sponsor was Spain
-He was the first to cross Panama to reach the Pacific Ocean.
Jacques Cartier:
-1531
-sponsor was France
-He sailed over 1,000 miles down the St. Lawrence River in Canada.
Henry Hudson:
-1607
-sponsor was England
-He sailed up the Hudson River in New York, but his crew turned against him.
What did a sponsor do for the explorers? paid for their trips
Monday, August 29, 2011
Native Americans: Hopi, Pawnee, and Seminole
To learn more about the Hopi, Pawnee, or Seminole, click their names.
Notes for quiz this week:
The Hopi lived in what region of the US? Southwest
What kind of houses did the Hopi live in? Pueblos
What is a peublo made of? mixture of dried clay
The Pawnee are from what region of the US? Plains
The Pawnee lived in _______________. Teepees
What did the Pawnee do to the buffalo skin they wore? painted it
What region are the Seminole from? Southeast
What kind of houses did the Seminole live in? Chickees
Why did the Seminole build their houses on top of poles? in case it flooded
Since it was so hot in the Southeast, the Seminole people wore ______________ clothing. light
*Parents: Keep reviewing these Native American notes with your children each night. Next week, we will have a cummalitive test on all of the tribes we covered.
Hopi Kochina dolls
Notes for quiz this week:
The Hopi lived in what region of the US? Southwest
What kind of houses did the Hopi live in? Pueblos
What is a peublo made of? mixture of dried clay
The Pawnee are from what region of the US? Plains
The Pawnee lived in _______________. Teepees
What did the Pawnee do to the buffalo skin they wore? painted it
What region are the Seminole from? Southeast
What kind of houses did the Seminole live in? Chickees
Why did the Seminole build their houses on top of poles? in case it flooded
Since it was so hot in the Southeast, the Seminole people wore ______________ clothing. light
*Parents: Keep reviewing these Native American notes with your children each night. Next week, we will have a cummalitive test on all of the tribes we covered.
Hopi Kochina dolls
Tuesday, August 23, 2011
Native Americans: Kwakiutl, Nez Perce, and Inuit
We are learning about 6 differnt tribes of Native Americans. So far, we have 3 tribes; Kwakiutl, Nez Perce, and Inuit. Click on the names of these tribes to learn more about them. Each student has a note 'packet' to use to study.
Notes for quiz this week:
What region are the Kwakiutl from? Northwest
What was a major natural resource for the Kwakiutl? Cedar Trees
What region are the Nez perce from? Plateau
What did the Nez Perce use for food and clothing? Deer
How were the Kwakiutl and Nez Perce alike? They both lived in long houses.
What region are the Inuit people from? Arctic
What was one way the Inuit kept warm? They ate whale fat.
What pole is the Arctic close to? North Pole
When it was really cold, what did the Inuit people live in? Igloos
What kinds of food did the Inuit people eat? seal, whale, caribou, and walrus
*Study your 'intersting facts' about each tribe.
Notes for quiz this week:
What region are the Kwakiutl from? Northwest
What was a major natural resource for the Kwakiutl? Cedar Trees
What region are the Nez perce from? Plateau
What did the Nez Perce use for food and clothing? Deer
How were the Kwakiutl and Nez Perce alike? They both lived in long houses.
What region are the Inuit people from? Arctic
What was one way the Inuit kept warm? They ate whale fat.
What pole is the Arctic close to? North Pole
When it was really cold, what did the Inuit people live in? Igloos
What kinds of food did the Inuit people eat? seal, whale, caribou, and walrus
*Study your 'intersting facts' about each tribe.
Tuesday, August 16, 2011
Native American Regions
Parents: We are beginning a 3 week unit on Native Americans. We will start by learning the different regions of the US that Native Americans lived in. We are also learning vocabulary for this unit. This weeks test will be over the vocabulary (your children have notes with the terms) and labeling the regions.
Students: Study your vocabulary! Here is a map with the regions. You can click here to go to the site we used in class to learn more about each region.
Vocabulary:
Glaciers: slow moving sheets of ice
When the Native Americans reached Alaska, glaciers blocked their path.
Migration: movement of people that takes place very slowly
The Native Americans migrated from Asia through North and South America.
Archaeologists: scientist who studies cultures of people from long ago
Archaeologists think that a land bridge existed between Asia and Alaska.
Artifacts: objects made by early people
An arrowhead is a Native American artifact.
Descendant: a person's relative who is born after they are
Native American decendants carry on a lot of the traditions from long ago.
Origin Stories: stories about the beginnings of Native American people
In one origin story, the world formed from a single grain of sand.
Ancestors: relatives that came before you
Native Americans have learned origin stories from their ancestors.
Nomads: wanderers who moved from place to place
Many Native Americans were nomads who followed their animals wherever they went.
Agriculture: farming; growing your own crops
When the Native Americans discovered agriculture, they could produce their own crops.
Tribe: group of Native Americans who share the same language and customs
There were over 80 different Native American tribes in the pacific northwest.
Pueblo: Native American homes
Some pueblos were built on the side of cliffs.
Time Line: shows events that took place during a certain period of time
Decade: 10 years
Century: 100 years
Millennium: 1,000 years
Students: Study your vocabulary! Here is a map with the regions. You can click here to go to the site we used in class to learn more about each region.
Vocabulary:
Glaciers: slow moving sheets of ice
When the Native Americans reached Alaska, glaciers blocked their path.
Migration: movement of people that takes place very slowly
The Native Americans migrated from Asia through North and South America.
Archaeologists: scientist who studies cultures of people from long ago
Archaeologists think that a land bridge existed between Asia and Alaska.
Artifacts: objects made by early people
An arrowhead is a Native American artifact.
Descendant: a person's relative who is born after they are
Native American decendants carry on a lot of the traditions from long ago.
Origin Stories: stories about the beginnings of Native American people
In one origin story, the world formed from a single grain of sand.
Ancestors: relatives that came before you
Native Americans have learned origin stories from their ancestors.
Nomads: wanderers who moved from place to place
Many Native Americans were nomads who followed their animals wherever they went.
Agriculture: farming; growing your own crops
When the Native Americans discovered agriculture, they could produce their own crops.
Tribe: group of Native Americans who share the same language and customs
There were over 80 different Native American tribes in the pacific northwest.
Pueblo: Native American homes
Some pueblos were built on the side of cliffs.
Time Line: shows events that took place during a certain period of time
Decade: 10 years
Century: 100 years
Millennium: 1,000 years
Tuesday, August 9, 2011
Maps and Direction
Parents: This week we are labeling all 50 states on a map. The students have a corresponding T-chart that list all states and their acronyms. We will be studying geography all year. I have asked the students to keep their map and chart in a safe place. If they keep up with it, they will be able to use them on test.
Students: Here are some questions you need to study for this weeks test.
What do all acronyms have to be? capital letters
What ocean is on the western side of the US? Pacific Ocean
What ocean is on the eastern side of the US? Atlantic Ocean
Boston, New York City, and Philadelphia are all in the ____________ region of the US. northeast
Is Mexico north or south of the US? south
Is Canada north or south of the US? north
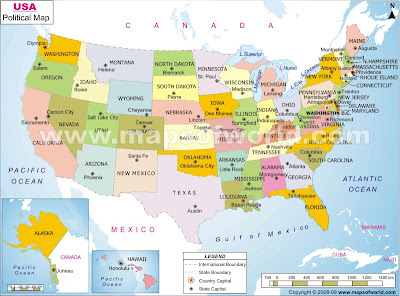
Political maps show _______________. political units(the way land is divided)
Physical maps show _________________. the way the land looks
*Remember students* I will be asking you what region and what direction different places are . If you do not know how to use your map and t-chart, you need to talk with me. You have to use them for the test!
Never Eat Soggy Waffles:
You also need to know where Boston, New York City, and Philadelphia are located.
Political map of the US
Physical map of the US
Students: Here are some questions you need to study for this weeks test.
What do all acronyms have to be? capital letters
What ocean is on the western side of the US? Pacific Ocean
What ocean is on the eastern side of the US? Atlantic Ocean
Boston, New York City, and Philadelphia are all in the ____________ region of the US. northeast
Is Mexico north or south of the US? south
Is Canada north or south of the US? north
Political maps show _______________. political units(the way land is divided)
Physical maps show _________________. the way the land looks
*Remember students* I will be asking you what region and what direction different places are . If you do not know how to use your map and t-chart, you need to talk with me. You have to use them for the test!
Never Eat Soggy Waffles:
You also need to know where Boston, New York City, and Philadelphia are located.
Political map of the US
Physical map of the US
Monday, August 1, 2011
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)